Linear regression the right way!
Notes taken listening to the lecture of Siraj Raval in udacity machine learning:
For our learning we use a dataset with student test scores and the amount of hours they study. There must be a relationship, the more you study the better the test scores become. We going to use linear regression to prove this relationship. The method used is gradient descent.
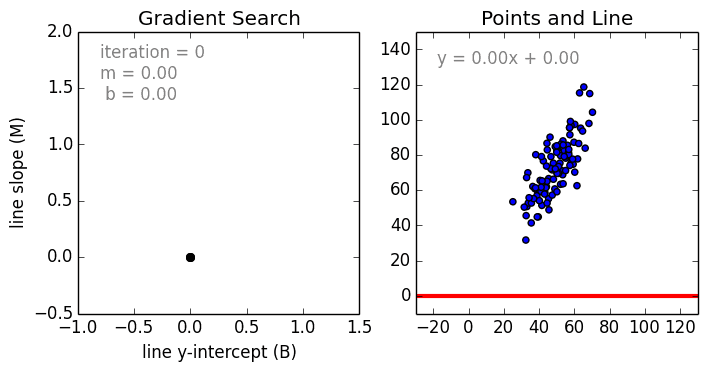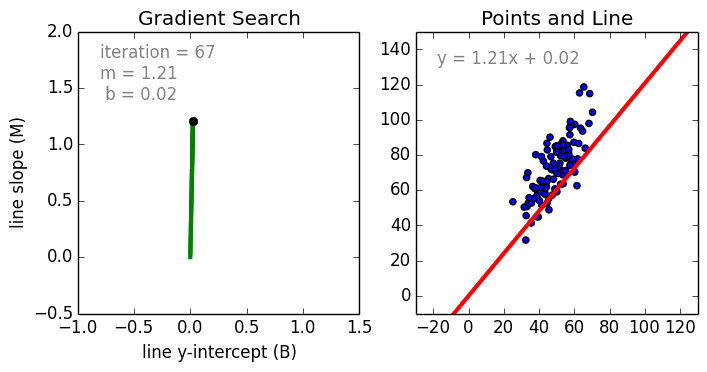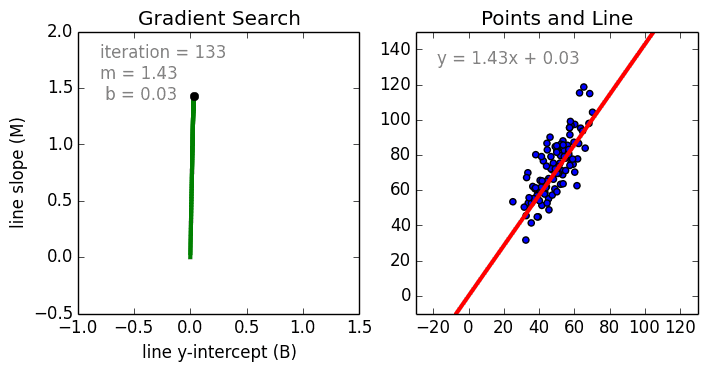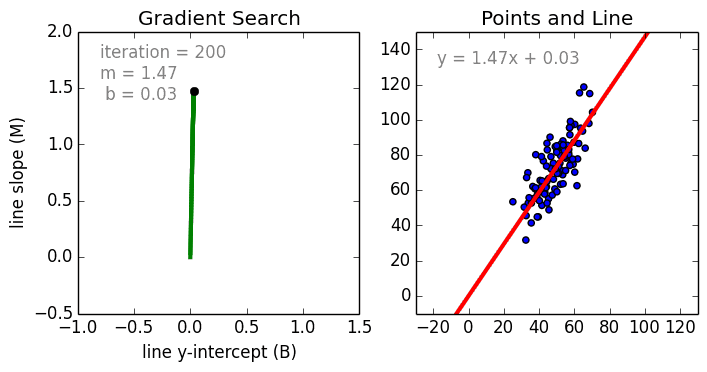
X is hours studied by the students Y is the test scored by the students
Hyperparameters: In machine learning these are the parameters that determine how our model is analyzing certain data, it is kind of tuning. There is a lot of hyperparameters and we going to use is learning_rate. It basically decides how fast should our model converge. Convergence means the point at which we get optimized result.
Other hyperparameters we going to use are
- Initial value of b
- Initial value of m
- Num_iterations = 1000 how much we are going to train this model a 1000 times as we just have 100 points in the data.
We perform gradient descent and this will give optimal slope and optimal y-intercept [b, m] = gradient_descent_runner(points, initial_b, initial_m, learning_rate, num_iterations)
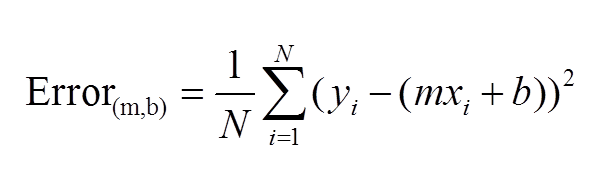
Calculates sum of set of values. (y-y)^2^ totalError += (y-(m * x + b))**2
We are trying to find a point at which the error is smallest , we call it gradient descent. Gradient is slope and we going to descent into that curvy bowl to reach a point that is optimal with least error. When error is smallest we have the line of best fit.
Partial derivative is shown below: http://mathinsight.org/image/partial_derivative_as_slope We are going to calculate partial derivative wrt b and m(to perform gradient descent). The black line is going to help us calculate the b and m value.
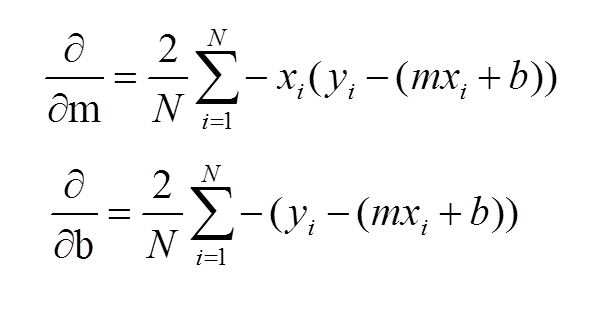 Explanation:
Gradient descent can be used to solve machine learning problems such as linear regression.
Gradient descent is an algorithm that minimizes functions. https://spin.atomicobject.com/2014/06/24/gradient-descent-linear-regression/
Explanation:
Gradient descent can be used to solve machine learning problems such as linear regression.
Gradient descent is an algorithm that minimizes functions. https://spin.atomicobject.com/2014/06/24/gradient-descent-linear-regression/
Gradient essentially means slope and mathematically slope is defined as the rate at which y-axis changes above the rate at which the x- axis changes. Or we can say the derivative of a function with respect to x. Descent means to go down or rather to go negatively down the gradient ascent. Gradient descent algorithm is an optimization technique where we find the local minimum of a function using its Gradient.